 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Call us on 443-686-9618
- Wish Lists
- My Account
- 0.00
Categories
- Home
- IHC Antibodies
- TH (Tyrosine hydroxylase) IHC Antibody
TH (Tyrosine hydroxylase) IHC Antibody
Product Description
Description |
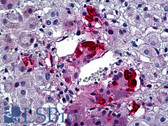
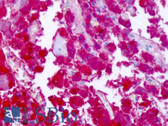
Tyrosine hydroxylase is involved in the conversion of phenylalanine to dopamine. As the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of catecholamines, tyrosine hydroxylase has a key role in the physiology of adrenergic neurons.Human TH gene contains 13 primary exons and spans approximately 8 kb.TH is in the 11p15.5 region. |
Catalog Number |
IW-MA1100 |
Quantity |
9 ml |
|
Host |
Mouse |
|
Clone |
TH-100 |
|
Isotype |
Mouse IgG1 |
|
Immunogen |
Rat tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). |
|
Purity |
Purified by the goat anti-mouse IgG affinity chromatography |
|
Conjugate |
Unconjugated |
|
Species Reactivity |
Human, rat. Not tested in other species. |
|
Positive Control |
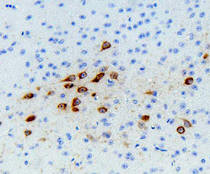
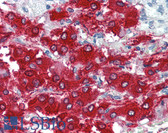
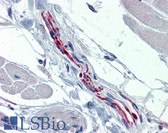
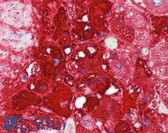
Brain (striatum, substantia nigra) |
|
Cellular Localization |
Cytoplasmic of dopamine neurons |
|
Form |
Ready to use solution in PBS with stabilizer and 0.01% sodium azide. No further dilution needed. Serum blocking step should be omitted. |
|
Storage |
Store at 2-8 °C. Do not freeze. |
|
Applications |
IHC-P: Heat induced epitope retrieval is required on formalin fixed paraffin embedded sections. IHC-Fr: Formalin or acetone fixed frozen sections. ICC: Not tested. |
|
Limitations |
This product is intended for Research Use Only. Interpretation of the test results is solely the responsibility of the user. |
|
Precautions |
Users should follow general laboratory precautions when handling this product. Wear personal protective equipment to avoid contact with skin and eyes. |
|
References |
1. Brilliant, M. H.; Niemann, M. M.; Eicher, E. M. : urine tyrosine hydroxylase maps to the distal end of chromosome 7 within a region conserved in mouse and man. J. Neurogenet. 4: 259-266, 1987. 2. Craig, S. P.; Buckle, V. J.; Craig, I. W.; Lamouroux, A.; Mallet, J. : Localization of the human tyrosine hydroxylase gene to chromosome 11p15. (Abstract) Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 40: 610 only, 1985. 3. Craig, S. P.; Buckle, V. J.; Lamouroux, A.; Mallet, J.; Craig, I. : Localization of the human tyrosine hydroxylase gene to 11p15: gene duplication and evolution of metabolic pathways. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 42: 29-32, 1986. |