 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Call us on 443-686-9618
- Wish Lists
- My Account
- 0.00
Categories
- Home
- IHC Antibodies
- MMP2 IHC Antibody
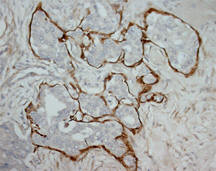
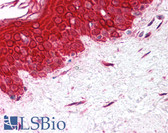
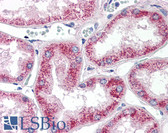
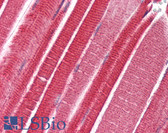
MMP2 IHC Antibody
Product Description
Description |
Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2) is a Type IV collagenase, 72-kD, which is also known as gelatinase1 and is a member of a group of secreted zinc metalloproteases2. The MMP2 gene is 17 kb long with 13 exons varying in size from 110 to 901 bp and 12 introns ranging from 175 to 4,350 bp 3, located within a region of human chromosome 16q13. In addition,The extra exons encode the amino acids of the fibronectin-like domain which has so far been found in only the 72- and 92-kDa type IV collagenase2. MMP2,which has a critical role in the binding of progelatinase A and TIMP4 via the C-terminal hemopexin-like domain (C domain)5, is functionally associated on the surface of angiogenic blood vessels6. NOT only is a likely effector of endometrial menstrual breakdown4, MMP2 is also effector and regulator of the inflammatory response7. Moreover, MMP2 could be helpful in diagnosing Takayasu arteritis.
|
Catalog Number
|
IW-PA1122 |
Quantity
|
9 ml |
|
Host
|
Rabbit
|
|
Clone
|
Polyclonal
|
|
Isotype
|
IgG
|
|
Immunogen
|
A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the C-terminal of human MMP2, identical to the related rat sequence.
|
|
Purity
|
Immunogen affinity purified
|
|
Conjugate
|
Unconjugated
|
|
Species Reactivity
|
Human, mouse, rat.Not tested in other species. |
|
Positive Control
|
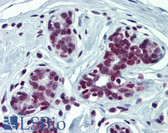
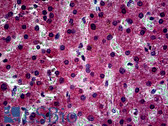
Human bladder carcinoma, human epidermal carcinoma, Human lymphadenoma, Rat intestine.
|
|
Cellular Localization
|
Cytoplasmic
|
|
Form
|
Ready to use solution in PBS with stabilizer and 0.01% sodium azide. No further dilution needed. Serum blocking step should be omitted.
|
|
Storage
|
Store at 2-8 °C. Do not freeze.
|
|
Applications
|
IHC-P: Formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue. Antigen retrieval by heat is required. IHC-Tek Epitope Retrieval Solution (IW-1100) is recommended. IHC-Fr: Formalin or acetone fixed frozen tissue. ICC: Acetone fixed cultured cells.
|
|
Limitations
|
This product is intended for Research Use Only. Interpretation of the test results is solely the responsibility of the user.
|
|
Precautions
|
Users should follow general laboratory precautions when handling this product. Wear personal protective equipment to avoid contact with skin and eyes.
|
|
References
|
1. Nagase, H.; Barrett, A. J.; Woessner, J. F., Jr. : Nomenclature and glossary of the matrix metalloproteinases. Matrix Suppl. 1: 421-424, 1992. 2. Collier, I. E.; Bruns, G. A. P.; Goldberg, G. I.; Gerhard, D. S. : On the structure and chromosome location of the 72- and 92-kDa human type IV collagenase genes. Genomics 9: 429-434, 1991. 3. Huhtala, P.; Chow, L. T.; Tryggvason, K. : Structure of the human type IV collagenase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 11077-11082, 1990. 4. Irwin, J. C.; Kirk, D.; Gwatkin, R. B. L.; Navre, M.; Cannon, P.; Giudice, L. C. : Human endometrial matrix metalloproteinase-2, a putative menstrual proteinase: hormonal regulation in cultured stromal cells and messenger RNA expression during the menstrual cycle. J. Clin. Invest. 97: 438-447, 1996. 5. Bigg, H. F.; Shi, Y. E.; Liu, Y. E.; Steffensen, B.; Overall, C. M. : Specific, high affinity binding of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-4 (TIMP-4) to the COOH-terminal hemopexin-like domain of human gelatinase A. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 15496-15500, 1997. 6. Brooks, P. C.; Silletti, S.; von Schalscha, T. L.; Friedlander, M.; Cheresh, D. A. : Disruption of angiogenesis by PEX, a noncatalytic metalloproteinase fragment with integrin binding activity. Cell 92: 391-400, 1998. 7. McQuibban, G. A.; Gong, J.-H.; Tam, E. M.; McCulloch, C. A. G.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Overall, C. M. : Inflammation dampened by gelatinase A cleavage of monocyte chemoattractant protein-3. Science 289: 1202-1206, 2000. 8. Matsuyama, A.; Sakai, N.; Ishigami, M.; Hiraoka, H.; Kashine, S.; Hirata, A.; Nakamura, T.; Yamashita, S.; Matsuzawa, Y. : Matrix metalloproteinases as novel disease markers in Takayasu arteritis. Circulation 108: 1469-1473, 2003.
|