 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Call us on 443-686-9618
- Wish Lists
- My Account
- 0.00
Categories
- Home
- IHC Antibodies
- COX2 IHC Antibody
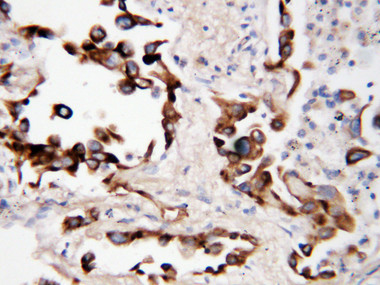
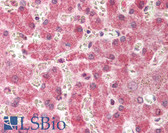
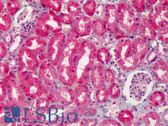
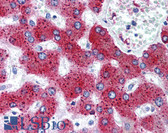
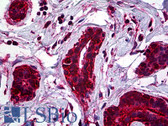
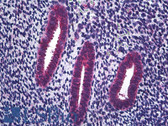
COX2 IHC Antibody
Product Description
Description |
Cyclooxygenase (Cox) is the key enzyme in conversion of arachidonic acid to PGs, and two isoforms, Cox-1 and Cox-2, have been identified.Cox-2 gene encodes an inducible prostaglandin synthase enzyme that is overexpressed in adenocarcinomas and other tumors. Deletion of the murine Cox-2 gene in Min mice reduced the incidence of intestinal tumors, suggesting that it is required for tumorigenesis. This gene is localized to sites associated with retinal blood vessels, and plays an important role in blood vessel formation in the retina.And the glucocorticoid receptor suppression of COX-2 is also crucial for curtailing lethal immune activation, and suggest new therapeutic approaches for regulation of T-cell-mediated inflammatory diseases.
|
Catalog Number
|
IW-PA1211 |
Quantity
|
9 ml |
|
Host
|
Rabbit
|
|
Clone
|
Polyclonal
|
|
Isotype
|
Rabbit IgG
|
|
Immunogen
|
A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the N-terminal of human COX2, different to the related rat sequence by two amino acids.
|
|
Purity
|
Immunogen affinity purified
|
|
Conjugate
|
Unconjugated
|
|
Species Reactivity
|
Human, mouse, rat. Not tested in other species. |
|
Positive Control
|
Human mammary cancer
|
|
Cellular Localization
|
Cytoplasmic
|
|
Form
|
Ready to use solution in PBS with stabilizer and 0.01% sodium azide. No further dilution needed. Serum blocking step should be omitted.
|
|
Storage
|
Store at 2-8 °C. Do not freeze.
|
|
Applications
|
IHC-P: Heat induced epitope retrieval is required on formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue sections. IHC-Fr: Not tested. ICC: Not tested.
|
|
Limitations
|
This product is intended for Research Use Only. Interpretation of the test results is solely the responsibility of the user.
|
|
Precautions
|
Users should follow general laboratory precautions when handling this product. Wear personal protective equipment to avoid contact with skin and eyes.
|
|
References
|
1. Salmenkivi, K.; Haglund, C.; Ristimaki, A.; Arola, J.; Heikkila, P. : Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in malignant pheochromocytomas. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 86: 5615-5619, 2001. 2. Liu, C. H.; Chang, S.-H.; Narko, K.; Trifan, O. C.; Wu, M.-T.; Smith, E.; Haudenschild, C.; Lane, T. F.; Hla, T. : Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 is sufficient to induce tumorigenesis in transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 18563-18569, 2001. 3. Wilkinson-Berka, J. L.; Alousis, N. S.; Kelly, D. J.; Gilbert, R. E. : COX-2 inhibition and retinal angiogenesis in a mouse model of retinopathy of prematurity. Invest. Ophthal. Vis. Sci. 44: 974-979, 2003. 4. Brewer, J. A.; Khor, B.; Vogt, S. K.; Muglia, L. M.; Fujiwara, H.; Haegele, K. E.; Sleckman, B. P.; Muglia, L. J. : T-cell glucocorticoid receptor is required to suppress COX-2-mediated lethal immune activation. Nature Med. 9: 1318-1322, 2003.
|