 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Call us on 443-686-9618
- Wish Lists
- My Account
- 0.00
Categories
- Home
- IHC Antibodies
- Anti-MYC / c-Myc Antibody (C-Terminus, clone 9E10) IHC-plus LS-B2791
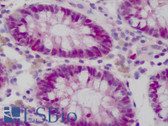
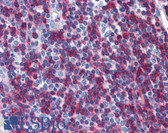
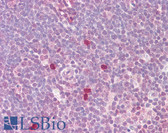
Anti-MYC / c-Myc Antibody (C-Terminus, clone 9E10) IHC-plus LS-B2791
$495.00
SKU:
LS-B2791