 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Call us on 443-686-9618
- Wish Lists
- My Account
- 0.00
Categories
- Home
- IHC Antibodies
- alpha-SMA IHC Antibody
alpha-SMA IHC Antibody
Product Description
Description |
Ueyama et al. (1990) assigned the ACTSA gene to chromosome 10 by Southern blot analysis of DNAs from 18 rodent-human somatic cell hybrids. Regional mapping by in situ hybridization localized the gene to 10q22-q24.Assignment of the vascular smooth muscle actin gene ACTSA to human chromosome .Smooth muscle alpha-actin gene requires two E-boxes for proper expression in vivo and is a target of class I basic helix-loop-helix proteins.
|
Catalog Number
|
IW-MA1106 |
Quantity
|
9 ml |
|
Host
|
Mouse
|
|
Clone
|
1A4
|
|
Isotype
|
Mouse IgG2a
|
|
Immunogen
|
N-terminal synthetic decapeptide of α-smooth muscle actin. |
|
Purity
|
Purified by the goat anti-mouse IgG affinity chromatography. |
|
Conjugate
|
Unconjugated
|
|
Species Reactivity
|
Human, mouse, rat. Not tested in other species. |
|
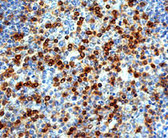
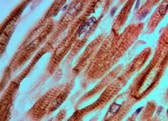
Positive Control
|
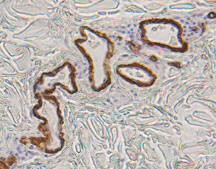
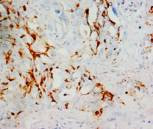
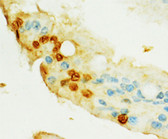
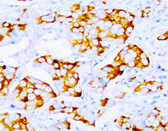
Smooth muscle, colon, skin, tonsil. |
|
Cellular Localization
|
Membrane/cytoplasmic
|
|
Form
|
Ready to use solution in PBS with stabilizer and 0.01% sodium azide. No further dilution needed. Serum blocking step should be omitted.
|
|
Storage
|
Store at 2-8 °C. Do not freeze.
|
|
Applications
|
IHC-P: Pretreatment is NOT required on formalin fixed paraffin sections. IHC-Fr: Not tested. ICC: Not tested.
|
|
Limitations
|
This product is intended for Research Use Only. Interpretation of the test results is solely the responsibility of the user.
|
|
Precautions
|
Users should follow general laboratory precautions when handling this product. Wear personal protective equipment to avoid contact with skin and eyes.
|
|
References
|
1. Kumar, M. S.; Hendrix, J. A.; Johnson, A. D.; Owens, G. K. : Smooth muscle alpha-actin gene requires two E-boxes for proper expression in vivo and is a target of class I basic helix-loop-helix proteins. Circ. Res. 92: 840-847, 2003. 2. Ueyama, H.; Bruns, G.; Kanda, N. : Assignment of the vascular smooth muscle actin gene ACTSA to human chromosome 10. Jpn. J. Hum. Genet. 35: 145-150, 1990.
|